الجمعة، 24 سبتمبر 2010
Mirror Image Effect In Photoshop
Step 1: Create A New Blank Document
Rather than working directly on the photo itself, let's start things off by creating a new blank document. This will allow us to create our effect at any size we need rather than trying to work within the dimensions of the photo itself. Go up to the File menu at the top of the screen and choose New, or simply press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+N (Win) / Command+N (Mac). Either way brings up Photoshop's New Document dialog box. Enter in the dimensions you need for your effect. For this tutorial, I'm going to enter in a standard size of 6 inches for the Width and 4 inches for the Height, but of course you can enter whatever dimensions you need. For the Resolution, I'll enter 240 pixels/inch, which should give me professional quality print results if I decide to print the image later. The most commonly accepted resolution for professional print results is 300 pixels/inch, but you'll often find that you can get away with less than that without any noticeably loss in quality. I typically use 240 pixels/inch with my images:
Step 2: Select And Copy The Photo
Switch over to the document window that contains the photo you're working with. We need to move the photo into our new blank document. There's a couple of ways we can do this, but we'll use the classic "copy and paste" method. First, we need to select the entire photo. Go up to the Select menu at the top of the screen and choose All, or press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+A (Win) / Command+A (Mac). This places a selection outline (also known as "marching ants") around the entire image in the document window:
With the entire photo now selected, go up to the Edit menu and choose Copy, or press Ctrl+C (Win) / Command+C (Mac) for the shortcut. This places the entire image temporarily into your computer's memory:

Step 3: Paste The Photo Into The New Document
Switch back over to your new blank document. We're going to paste the photo into it. To do that, go back up to the Edit menu and this time, choose Paste. Or press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+V (Win) / Command+V (Mac):

If we look in the Layers palette for the new document, we can see that our photo has been placed on its own layer above the Background layer. Photoshop has automatically named the layer "Layer 1":

Step 4: Resize And Reposition The Photo Inside The Document If Needed
You'll probably find that the photo doesn't fit perfectly inside the new document. In my case, the photo is too big and part of it is extending out beyond the document's visible area. We'll need to resize it, and for that, we can use Photoshop's Free Transform command. Go up to the Edit menu and choose Free Transform, or press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+T (Win) / Command+T (Mac):

Either way brings up the Free Transform box and handles around the image. Unfortunately, since part of my photo is extending out beyond the document's visible area, I can't see all of the Free Transform handles. To fix that, I'll simply go up to the View menu at the top of the screen and choose Fit on Screen. I could also select the same option with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+0 (Win) / Command+0 (Mac):

The Fit on Screen command zooms the image out far enough so that everything, including the Free Transform handles, are now visible inside the document window. To resize the image, hold down your Shift key, then click and drag any of the corner handles inward until you have as much of the image as you need inside the visible area. Holding down the Shift key as you drag constrains the aspect ratio of the image so you don't accidentally distort the shape of it. In my case, I'm going to click on the handle in the bottom right corner and drag it inward until the bottom of the photo lines up with the bottom of the visible area:

You can also move the image as needed to reposition it by clicking anywhere inside the Free Transform box and dragging the image around. Just don't click on the small target symbol in the center of the Free Transform box, otherwise you'll move the target symbol, not the image. When you're done, press Enter (Win) / Return (Mac) to accept the changes and exit out of the Free Transform command.
To zoom the image back in so it once again fills up the entire document window, simply choose Fit on Screen again from the View menu just as we did a moment ago. You can also select Actual Pixels from the View menu, which will zoom the image to a full 100%. The keyboard shortcut for Actual Pixels is Ctrl+Alt+0 (Win) / Command+Option+0 (Mac).
Step 5: Add A Vertical Guide Down The Middle Of The Document
To create our mirror image effect, we first need to move everything that we want to "mirror" over to one side of the document. In my case, I need the guy in my photo to be over on the left side. To help me decide exactly how far to the left I need to move him, I'm going to add a guide down the middle of the image. Go up to the View menu at the top of the screen and choose New Guide:

his brings up photoshop 


Don't worry about the guide appearing in front of your image. It's there only to help us while working in Photoshop. Guides are known as "non-printing elements", which means they won't print, or appear if you save the image for the web, even if you forget to remove them when you're done.
Step 6: Drag Your Main Subject To One Side Of The Document
Think of the guide we just added as the "flip point" or "mirror point" for the effect. In other words, everything that we place on one side of the guide will appear mirrored on the other side of it. Of course, before we can mirror anything, we first need to move everything we want to mirror over to one side of the document. Select the Move tool from the top of the Tools palette, or press the letter V to quickly select it with the shortc
:

Then, with the Move tool selected, click anywhere on the image and drag it left or right until everything you want to mirror is on one side of the guide. Hold down the Shift key as you drag, which will force the image to move only left or right, preventing you from accidentally moving it up or down. In my case, I'm going to drag the guy in my photo over to the left of the document just to the point where the bottom part of his ear touches the side of his face. This is going to be the "flip point" for my effect:

Don't worry about the solid white area that's now appearing on the side of the photo. Everything on that side of the guide will be replaced with a mirrored version of what's on the other side in a moment.
Step 7: Drag A Selection Around The Side You Want To Mirror
Select the Rectangular Marquee Tool from the top of the Tools palette, or press the letter M to select it with the keyboard shortcut:

Then, with the Rectangular Marquee Tool selected, drag a selection around the entire half of the document that you want to mirror. In my case, I'm going to drag a selection around the left half of the document. You'll find that your cursor will snap to the guide once you're close enough to it (as long as you have both the Snap and Snap to Guides options enabled in the View menu at the top of the screen). When you're done, you should have a selection outline around the entire half of the document that you're going to mirror:

Step 8: Copy The Selection To A New Layer
With the side that's going to be mirrored now selected, go up to the Layer menu at the top of the screen, choose New, and then choose Layer via Copy. Or press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+J (Win) / Command+J (Mac):

This creates a copy of the selection and places it on a new layer directly above the previous layer. Nothing will seem to have happened in the document window, but if we look in the Layers palette, we can see that we now have a new layer named "Layer 2", and if we look in the layer's preview thumbnail to the left of the layer's name, we can see that the layer contains a copy of the side of the document we had selected:

Step 9: Flip The Left Or Right Side Of The Document Horizontally
To create our mirrored image effect, all we need to do at this point is flip the half of the document that's on "Layer 2" horizontally. Before we do that, though, we need to tell Photoshop that we want to use the vertical center of the document (where the guide is) as the "flip point". To do that, press Ctrl+T (Win) / Command+T (Mac) to quickly bring up Photoshop's Free Transform command once again. You'll see the Free Transform box and handles appear around whichever side of the document you copied to "Layer 2". In my case, it's the left side. See that little target symbol in the center of the Free Transform box, the one I told you not to click on earlier:

That target symbol represents the rotation point for the Free Transform command. By default, it's located in the center of the Free Transform box, but we can move it anywhere we want. Wherever we move it to becomes the new rotation point. To tell Photoshop that we want to flip the image along the guide, simply click on the target symbol and drag it over to the side handle that's sitting directly in the middle of the document. Once you get close enough to the handle, the target symbol will snap to it:

With the Free Transform command still active, go up to the Edit menu at the top of the screen, choose Transform, and then choose Flip Horizontal:

Photoshop flips the contents of "Layer 2" for us, using our newly repositioned target symbol as the rotation point, and the right half of the document now becomes a perfectly mirrored copy of the left half

Press Enter (Win) / Return (Mac) to accept the transformation and exit out of the Free Transform command. We don't need our guide anymore, so go up to the View menu and choose Clear Guides:

As I mentioned earlier, even if you forget to clear your guides when you're done working on the image, there's no need to worry because they won't print and they won't appear in the image if you save it for the web.
And with that, we're done! Here, after just a few simple steps, is our completed "mirror image" effect:

And there we have it!
Untouched Signature Photoshop Tutorial
Final Preview
Download source file: http://creativeoverflow.net/resources/tutorials/untouched/psd_untouched.rar
Create a Realistic Soda Bottle in Photoshop
Step 1
Create a new document 600 x 800 pixels with a Resolution of 72 dpi. With the Pen tool, draw the outline of half the bottle. I recommend grabbing an image of a bottle to use as a reference. This tutorial does not use any outside images or resources but it may help to use an image of a bottle to get an idea of how the outlook will be.Now create a selection of the path you just created by Cmd + click on the layer in the Paths palette. You can fill this selection with any color you want, depending on what kind of bottle you are creating. But in this case I filled it with #872a12.
Step 2
Now duplicate the layer by right clicking on it in the Layers palette and clicking Duplicate Layer. Take the new layer and press Cmd + T to Free Transform it. Move it over to the right side of the original layer and continue to stay in Free Transform mode. Right-click on the screen and Flip Horizontal. Press Enter to exit Free Transform. Now highlight the 2 layers and press Cmd + E to merge them together. Call this Layer Outer Bottle Shape.Step 3
We are going to start making highlights and shadows on the bottle to give it more of a 3D look. For the top part of the bottle grab the Elliptical Marquee Tool and drag it out near the top of the bottle, as shown in the image below. Take the Burn tool and bring down the Exposure to around 20% and set the Range to Midtones. With a very soft brush start brushing the inside of the selection and create a soft line across the top of it.Now inverse the selection by pressing Cmd + Shift + I. Take the Dodge tool with the same hardness of 0 and brush across the selection as shown in the 2nd image below. This will give the bottle a nice ridge effect. You can touch up this area by also using the Dodge tool on the other side as well.
Step 4
Start adding some highlights along the side of the bottle. First grab the Burn tool with a soft brush. Exposure set to around 20% and Range set to Midtones. Start brushing along the side of the bottle to give it a nice shadow. Take the Dodge tool with the same settings and brush on the inside of where you used the Burn tool.Step 5
Duplicate the layer and name it Noise. Add some noise by going to Filter > Noise > Add Noise. Set the Amount to around 12%, with Gaussian and Monochromatic checked. Set the Blending Mode of this layer to Overlay and bring the Opacity down to around 15%. If you feel there is too much noise on the bottle you can take a soft Eraser brush with low Opacity and erase some of the noise away. This will give it a nice subtle textured look.Step 6
Let’s add some liquid inside the bottle. Go back to the first layer called Outer Bottle Shape and duplicate it, call this layer Liquid. Cmd + T on the new layer to enter Free Transform mode. Hold down Alt + Shift and slightly bring down the size. Press the Down Arrow key a few times to align the Liquid layer near the bottom of the bottle.Now take the Rectangular Marquee Tool and delete the top part of the Liquid layer, as shown in the image below. Drag out the selection over the area that you want deleted and hit the Delete key.
We will now add a gradient overlay to this layer. With the Liquid layer still selected, go into the Layer Style window. To do this you can either double click on the layer or go to Layer > Layer Style > Gradient Overlay. The only settings you will need to change are the colors. Set the Blending Mode of this layer to Overlay and bring the Opacity down to around 30%
Step 7
Create a new layer on top of the Liquid layer and name it Liquid Top. Grab the Elliptical Marquee Tool and drag it out over a small area above the liquid, as shown in the image below. Fill it with a dark color (#791c0c) and add a Gaussian Blur. Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur. Set the Radius to 2 pixels. Bring the Opacity down to around 70%.Step 8
Now we’ll start creating the outter ridges of the bottle. Create a new layer called Ridge and with the Pen tool draw where you think the ridge on the bottle will be. This would be a good time to consult your reference image as to where the details and textures are. Make a selection of the path and give it a Feather of 1. Select > Modify > Feather.Fill with a lighter color, keep the selection highlighted and grab your Burn tool. Start brushing the edges of the selection with the Burn tool but try not to overdo it. Also make a nice highlight with the Burn tool at the bottom of the selection to make it look like the ridge is sticking out. Do the same with the Dodge tool except use the brush down the middle of the selection.
To make it look like the ridge is attached to the bottle, erase the top of the selection with a very soft brush. The Opacity of the brush should be about 40%.
Step 9
Repeat Step 8 by creating more ridges along the bottle until it looks similar to the image below. If you want your layers to stay organized, you can put all of the Ridge layers into a Folder and name it Top Ridges.Step 10
Now it’s time to create the bottom ridges of the bottle. Repeat Step 8 except in this case these ridges will extend out to the bottom of the bottle. When using the Pen tool, draw the ridge to stay consistent with the flow and shape of the bottle.When you are done creating the highlights and shadows of the first ridge, duplicate the layer. Ctrl + T the layer and move it over to the right side of the bottle, then right-click on it and Flip Horizontal. When creating the middle ridge, use a soft Eraser brush with low opacity to erase away the bottom of the layer.
Step 11
Now add some more glare and highlights to the bottle. Duplicate the Outter Bottle Shape layer and call it Highlights. Take your Dodge tool and raise the Exposure to about 25% or 30% with a soft brush. Start painting the bottle down the middle and a bit on the sides. Now take the Burn tool and do the same thing around the sides and bottom of the bottle.Step 12
Now it’s time to create the cap for the bottle. Create a new layer called Cap. Use the Pen tool to draw out a selection on top of the bottle. Fill the selection with a red color, I used #ce1831.To create the small ridges in the cap use the Dodge and Burn tools. With the Dodge tool selected use a very small brush with a Hardness of about 20% and create the outter ridges of the cap, shown in image below. Do the same thing with the Burn tool to create the small inner ridges.
Take the Dodge tool and create a very soft highlight on top of the cap. Create a new layer under the Cap layer and name it Shadow. Take the Brush tool with a color of Black and hardness of 0. Paint in behind the cap and turn down the opacity to about 70%.
Step 13a
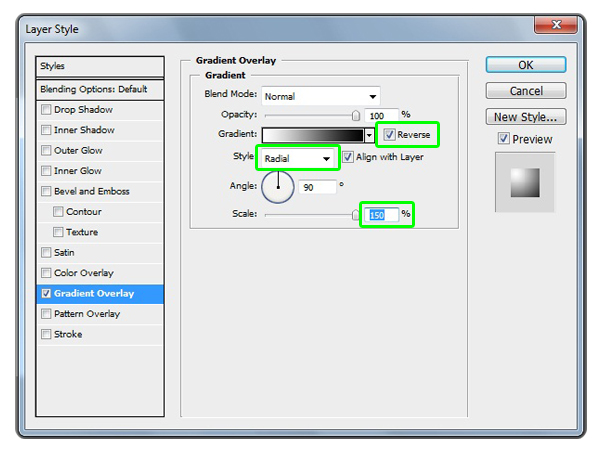
Now it’s time to create the condensation (bubbles). To do this, we will create a new brush preset. Create a new document 300 x 300 pixels with a Resolution of 72. Create a new layer and call it Bubble. With the Elliptical Marquee Tool create a circle the size of the document. Remember to hold down shift when creating the circle to make it perfect. Fill the selection with white.Let’s apply a few Layer Styles to this Bubble layer. Layer > Layer Style > Gradient Overlay and add the following settings in the image below. When you are applying the Gradient Overlay take the cursor over the Bubble image and move the gradient to the upper left area of the bubble.
Then add an Inner Glow layer style with the same settings as the image below.
Step 13b
On the Layer Palette, right-click on the Effects of the Bubble layer and choose Create Layers (a). This will turn the Layer Styles to Layers. Then select all of the layers (b) and merge them together by pressing Ctrl + E (c).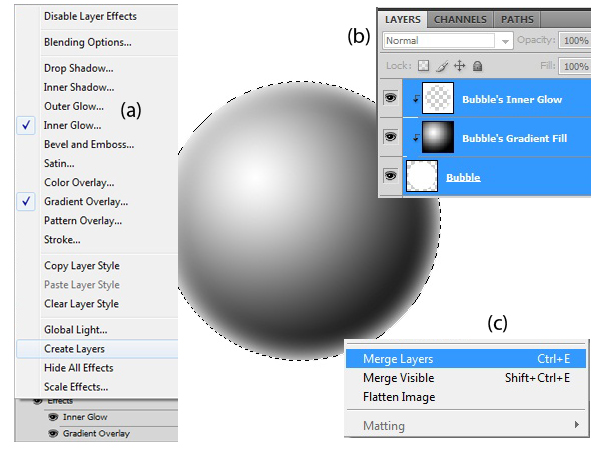
Step 13c
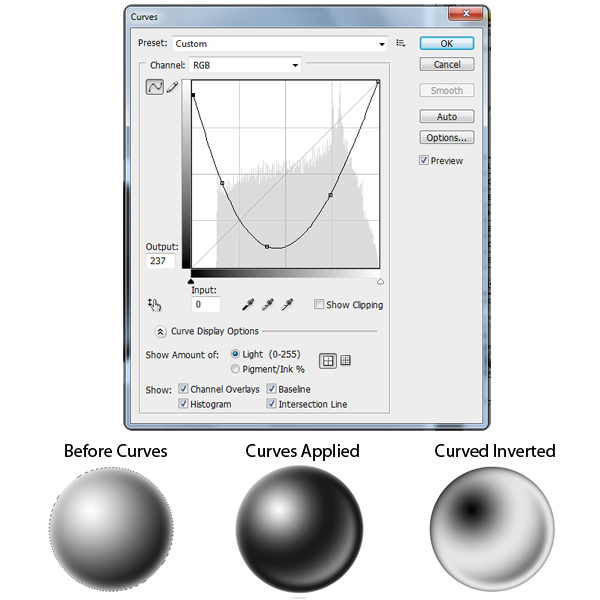
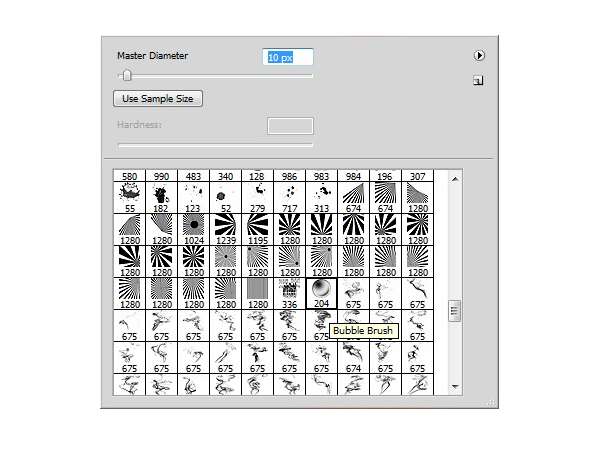
Now we’re going to change how the bubble looks. Go to Image > Adjustments > Curves and change the settings similar to the image below. Once you have applied the Curves to the Bubble layer go to Image > Adjustments > Invert.To turn this Bubble layer into a Brush Preset, go to Edit > Define Brush Preset and name it Bubble.
Step 14
Now go back to your original document and select your new Bubble Brush that you have just created. Create a new layer and use a small brush size of around 10 pixels and a color of white. Start brushing in the bubbles onto the bottle. Try not to make all of the bubbles the same size. Use the ‘ [ ' and ' ] ‘ keys to quickly change the size of the brush.Now take the Smudge tool with a Strength of around 25% and start brushing away some of the bubbles. This will give the bubbles a cool drip effect.
When you are done, set the Blending Mode to Overlay and duplicate the layer. Set the new layer’s Blending Mode to Normal and bring back the Opacity to about 33%.
Step 15a
Now it’s time to add a label. I created a custom label but you can use whatever you want. Make sure the label is approximately the same size as the middle indented area of the bottle.
Step 15b
Click on the Label layer and go to Edit > Transform > Warp. Bring back the Opacity of the layer to about 50% so you can see the bottle. Grab each corner of the Warp window and bring it in, adjust it until the label fits perfectly onto the bottle.Once the label is nicely fitted to the bottle use the Burn and Dodge tools to give the label some nice highlights and shadows.

Step 16
For the background I just used a simple gradient of dark to light blue.
Step 17a
Finally, I added a reflection to the bottom of the image. Duplicate the Outer Bottle Shape layer and bring it to the bottom on the layers palette. Rename this layer Reflection. Press Cmd + T and right-click on it, Flip Vertical. Press the Down Arrow keys until it is placed just underneath the bottle image and press Enter to exit Free Transform.Now take the Eraser tool with a soft brush and erase away some of the edges. Turn down the opacity to around 60%
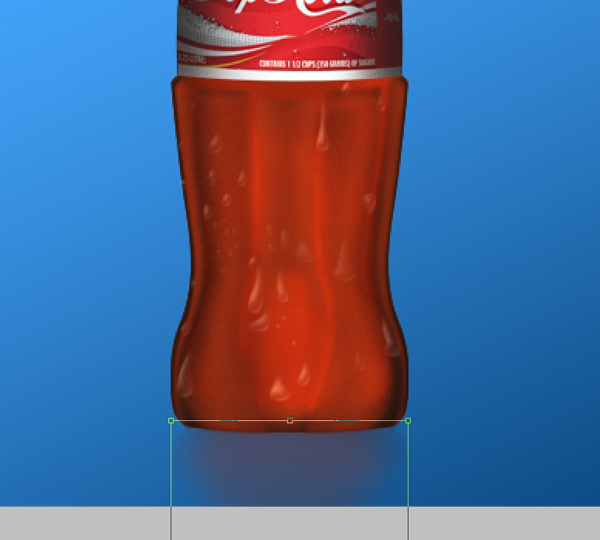

Step 17b
Next make a new layer above the Reflection layer and name it Reflection Blur. Take the Polygonal Lasso Tool and create a quick shape around the bottom of the bottle, shown in the image below. Ctrl + D to Deselect it and go to Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur. Give it a Radius of 12 pixels and set the Blending Mode to Overlay and set the Opacity to about 50%.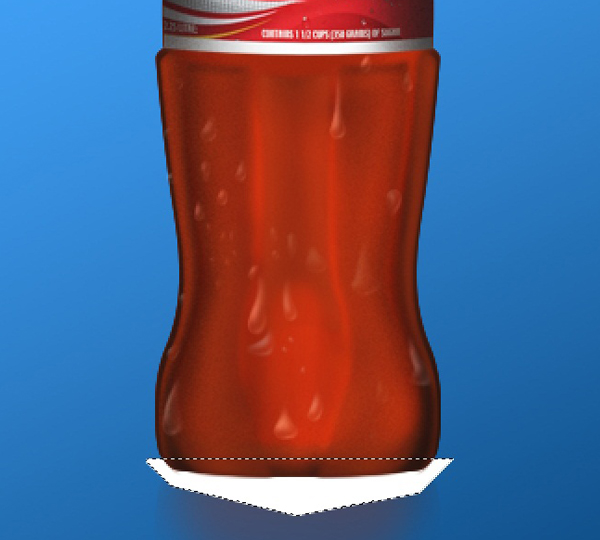
Conclusion
The more you use tools like Pen, Dodge, and Burn the better you’ll become with them. Hopefully this tutorial has given you some practice and has inspired you to create different types of objects using similar styles and techniques.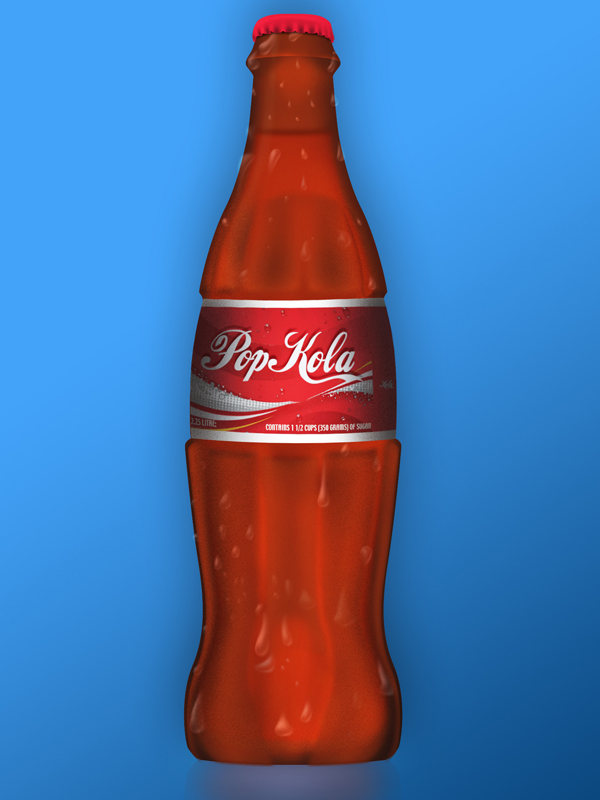
Source:http://psd.tutsplus.com/tutorials/drawing/create-a-realistic-soda-bottle-in-photoshop/
الاشتراك في:
التعليقات (Atom)


























